一、本文目的
本文仅关注 AARCH64 FP 栈回溯过程,Arm32 下栈回溯方案及其适用范围不在本文讨论范围。
二、AARCH64 栈帧结构
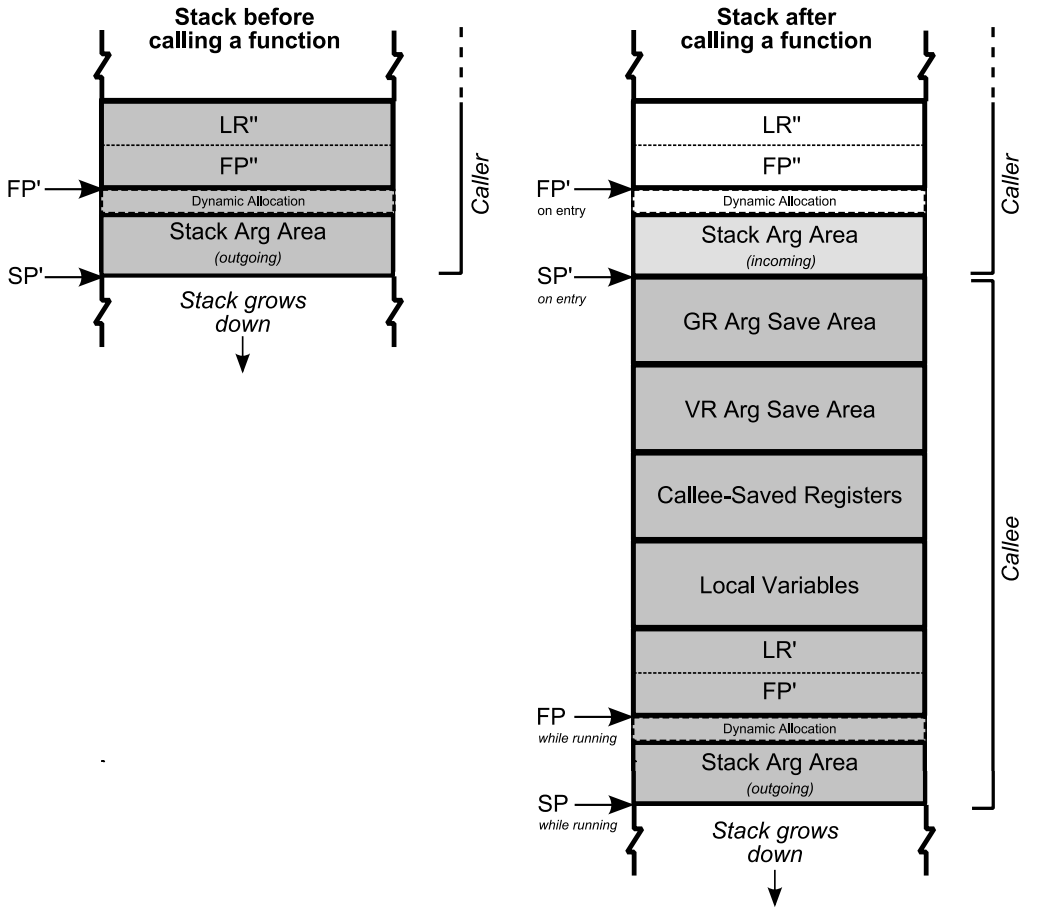
栈帧结构如图,下面通过一个简单的示例,看下栈帧开辟、释放及寄存器值保存和恢复的过程。
2.1 示例
一个简单函数调用的例子,代码如下:
void fun2(int a){
int c = a + 1;
printf("Hello world!");
}
void func1()
{
fun2(1);
}
其汇编代码如下:
.text
.file "call_test.c"
.globl fun2 // -- Begin function fun2
.p2align 2
.type fun2,@function
fun2: // @fun2
// %bb.0:
sub sp, sp, #32 // =32
stp x29, x30, [sp, #16] // 16-byte Folded Spill
add x29, sp, #16 // =16
adrp x8, .L.str
add x8, x8, :lo12:.L.str
stur w0, [x29, #-4]
ldur w9, [x29, #-4]
add w9, w9, #1 // =1
str w9, [sp, #8]
mov x0, x8
bl printf
ldp x29, x30, [sp, #16] // 16-byte Folded Reload
add sp, sp, #32 // =32
ret
.Lfunc_end0:
.size fun2, .Lfunc_end0-fun2
// -- End function
.globl func1 // -- Begin function func1
.p2align 2
.type func1,@function
func1: // @func1
// %bb.0:
stp x29, x30, [sp, #-16]! // 16-byte Folded Spill
mov x29, sp
mov w0, #1
bl fun2
ldp x29, x30, [sp], #16 // 16-byte Folded Reload
ret
.Lfunc_end1:
.size func1, .Lfunc_end1-func1
// -- End function
.type .L.str,@object // @.str
.section .rodata.str1.1,"aMS",@progbits,1
.L.str:
.asciz "Hello world!"
.size .L.str, 13
.ident "Android (7019983 based on r365631c3) clang version 9.0.9 (https://android.googlesource.com/toolchain/llvm-project a2a1e703c0edb03ba29944e529ccbf457742737b) (based on LLVM 9.0.9svn)"
.section ".note.GNU-stack","",@progbits
汇编 func2 前三行代码为扩栈及保存 caller 函数的 sp、fp、lr,后两行代码为恢复 caller 函数的 sp、fp、lr。
ARM64汇编中有34个寄存器,其中包含31个通用寄存器(x0-x30),sp,pc和cpsr。 X29 就是 FP 寄存器 X30 就是 LR 寄存器
2.1.1 开辟栈空间
sub sp, sp, #32 // =32
sp 寄存器中的值减去 0x32 之后保存到 sp 寄存器。 linux 栈空间栈低在高地址,栈顶在低地址因此扩展需要用 sub。
stp x29, x30, [sp, #16] // 16-byte Folded Spill
将 x29(fp)、x30(lr) 寄存器中的值保存到 sp + 0x16 中。 stp 是一个组合指令,可以同时操作两个寄存器。
add x29, sp, #16
sp 中的值加上 0x16 保存到 x29。 开辟的栈空间大小是 0x32,其中 0x16 用于保存上个函数的 fp 及 lr。 因此还剩 0x16,当前栈顶 + 0x16 即为新的栈底。
2.2.2 函数出栈
ldp x29, x30, [sp, #16] // 16-byte Folded Reload
恢复上个函数的 fp、lr 到 x29 和 x30 寄存器。
add sp, sp, #32
将当前函数栈帧从栈中移除。
2.2.3 小结
- 每次函数调用都会有开辟栈空间和移除当前栈帧的过程。
- 开辟栈空间后需要将 caller 的 fp、lr 保存到栈中,同时计算出新函数的栈底。
- 函数返回时从栈中恢复 caller 的 fp、lr,同时将当前栈帧从栈中移除。
三、FP 栈回溯
从前面栈帧结构我们可以看到当前栈的栈底(FP)之前的两条数据分别为上个函数的 FP 和 LR。 只需要找到当前函数的 FP 就可以计算出当前线程的函数调用过程。
3.1 示例
typedef struct {
uintptr_t fp;
uintptr_t lr;
} frame_record_t;
void print_method_info(uintptr_t pc_addr) {
if (0 != pc_addr) {
void *cache = NULL;
Dl_info info;
memset(&info, 0, sizeof(Dl_info));
// 通过 linker 获取符号信息
dladdr((void *) (pc_addr), &info);
__android_log_print(ANDROID_LOG_INFO, "Z_UNWIND",
"pc %08" PRIxPTR " %s (%s+%" PRIuPTR ")\n",
pc_addr - (uintptr_t) info.dli_fbase, info.dli_fname,
info.dli_sname,
pc_addr - (uintptr_t) info.dli_saddr);
}
}
static inline uintptr_t clear_pac_bits(uintptr_t addr) {
register uintptr_t x30 __asm__("x30") = addr;
__asm__("xpaclri" : "+r"(x30));
return x30;
}
size_t unwind() {
// 获取当前 FP
uintptr_t cur_fp = (uintptr_t) (__builtin_frame_address(0));
// 回溯
while (1) {
uintptr_t prev_fp;
frame_record_t *record = (frame_record_t *) cur_fp;
uintptr_t real_addr = clear_pac_bits(record->lr < 4 ? 0 : record->lr - 4);
//打印当前符号信息
print_method_info(real_addr);
prev_fp = record->fp;
if (prev_fp & 0xfu) break;
// ensure to walk FP from low address to high address
if (prev_fp < cur_fp + sizeof(frame_record_t)) break;
// 继续到下一个栈帧
cur_fp = prev_fp;
}
return 0;
}
static void sample_sigabrt_handler(int signum, siginfo_t *siginfo, void *context) {
(void) signum, (void) siginfo;
unwind();
__android_log_print(ANDROID_LOG_INFO, "Z_UNWIND", "\n");
}
static void sample_signal_register(void) {
struct sigaction act;
memset(&act, 0, sizeof(act));
sigfillset(&act.sa_mask);
sigdelset(&act.sa_mask, SIGSEGV);
act.sa_sigaction = sample_sigabrt_handler;
act.sa_flags = SA_RESTART | SA_SIGINFO | SA_ONSTACK;
sigaction(SIGABRT, &act, NULL);
}
void func4(int a, int b, int c, int d, int e) {
tgkill(getpid(), gettid(), SIGABRT);
// unwind();
// __android_log_print(ANDROID_LOG_INFO, "BOBO_UNWIND", "\n");
}
void func3(int a, int b, int c, int d, int e, int f, int g, int h) {
func4(1, 2, 3, 4, 5);
}
void func2(int a, int b, int c) {
func3(1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8);
}
void func1(int a) {
func2(1, 2, 3);
}
extern "C" JNIEXPORT jstring JNICALL
Java_com_example_androidunwinddemo_MainActivity_stringFromJNI(
JNIEnv *env,
jobject /* this */) {
sample_signal_register();
func1(1);
std::string hello = "Hello from C++";
return env->NewStringUTF(hello.c_str());
}
整体逻辑比较简单: func1 call fun2 call func3 call func4。 信号处理或直接调用 unwind,unwind 中找到当前 fp,计算出上一个栈帧的 fp、lr。 通过 linker 找到当前符号信息并打印。
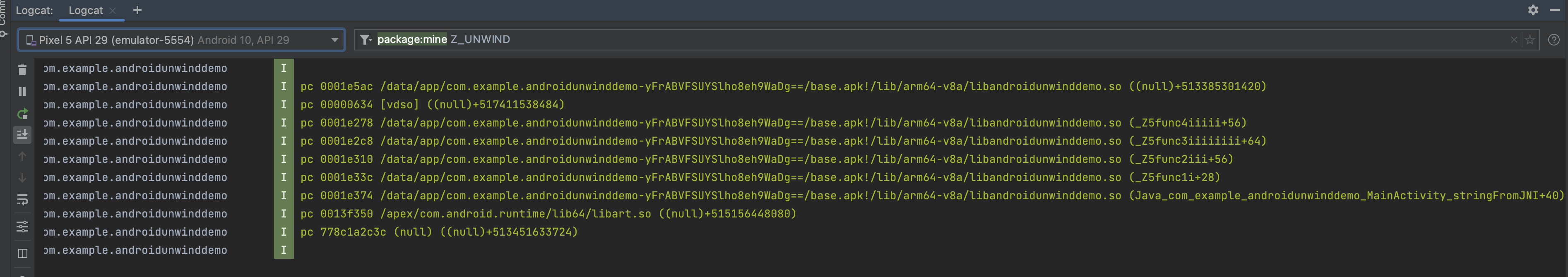
结果如下: