注意
- 本文基于 WebRTC M89
带宽探测
带宽探测在带宽大幅下降时被调用,相关的类有 ProbeController 和 ProbeBitrateEstimator。带宽探测的原理是以 cluster_id 为单位以一定速率发送 RTP 包,收到反馈消息后根据发送_接收数据除以间隔时间计算出发送端_接收端的「带宽」,最后取它们俩中的较小的值作为探测到的带宽。
带宽探测包 feedback 消息处理的方法是 ProbeBitrateEstimator::HandleProbeAndEstimateBitrate。
拥塞控制
WebRTC 中移除了之前用过的 BBR ,现在用的是 Google congestion control。移除 BBR 的的原因个人理解是 BBR 在与基于丢包的拥塞控制算法竞争中处于劣势。 Google congestion controller 中有两种方式实现拥塞控制——基于丢包和基于延迟,基于丢包的拥塞控制算法默认不开启,本文只分析基于延迟的拥塞控制算法既 DelayBasedBwe。 相关的类有:
- GoogCcNetworkController
- DelayBasedBwe
- TrendlineEstimator
- AimdRateControl
Google congestion control 从接收到 feedback 到将目标码率应用到 sender 、encoder 要经历以下几个步骤:
- 根据 feedback 计算时延梯度
- 时延梯度平滑处理后根据线性回归(最小二乘法)计算出网络趋势
- 根据趋势「探测」出网络状态
- 根据网络状态计算出目标带宽
- 综合 DelayBasedBwe 和 LinkCapacityTracker 计算出的带宽计算出 TargetTransferRate。
- 将 TargetTransferRate 应用到 sender 和 encoder 。
时延梯度
WebRTC 中计算延时不是按包计算的,而是通过将包分组,然后计算包组间的延时。 WebRTC 根据包发送时间来分组,在包组中后续包距第一个包的发送时间差小于 5ms。如果某个包和包组中首包的发送时间差大于 5ms,那么这个包就作为下一个包组的第一个包。
brust
WebRTC 发送端实现了平滑发送,所以理论上不存在 brust,但是在 wifi 网络下某些 wifi 设备的转发模式是,在某个固定时间片内才有机会发送数据。在等待时间片的时候数据包堆积,在发送时形成 brust ,这个 brust 中所有的数据被视为一组。
包组时延梯度
包组时间差是指不同包组网络时间的的差值。 eg: 两组包到达时间差为:
t(i) - t(i-1)
两组包发送时间差为:
T(i) - T(i-1)
包组时延变化为:
d(i) = t(i) - t(i-1) - (T(i) - T(i-1))
这个时延变化将会用于 TrendlineEstimator,用来时延增长趋势,判断网络拥塞状况。
线性回归
平滑处理
smoothed_delay_ = smoothing_coef_ * smoothed_delay_ +
(1 - smoothing_coef_) * accumulated_delay_;
这里平滑使用的是 moving average,smoothing_coef_ 默认值是 0.9。
最小二乘法计算网络趋势
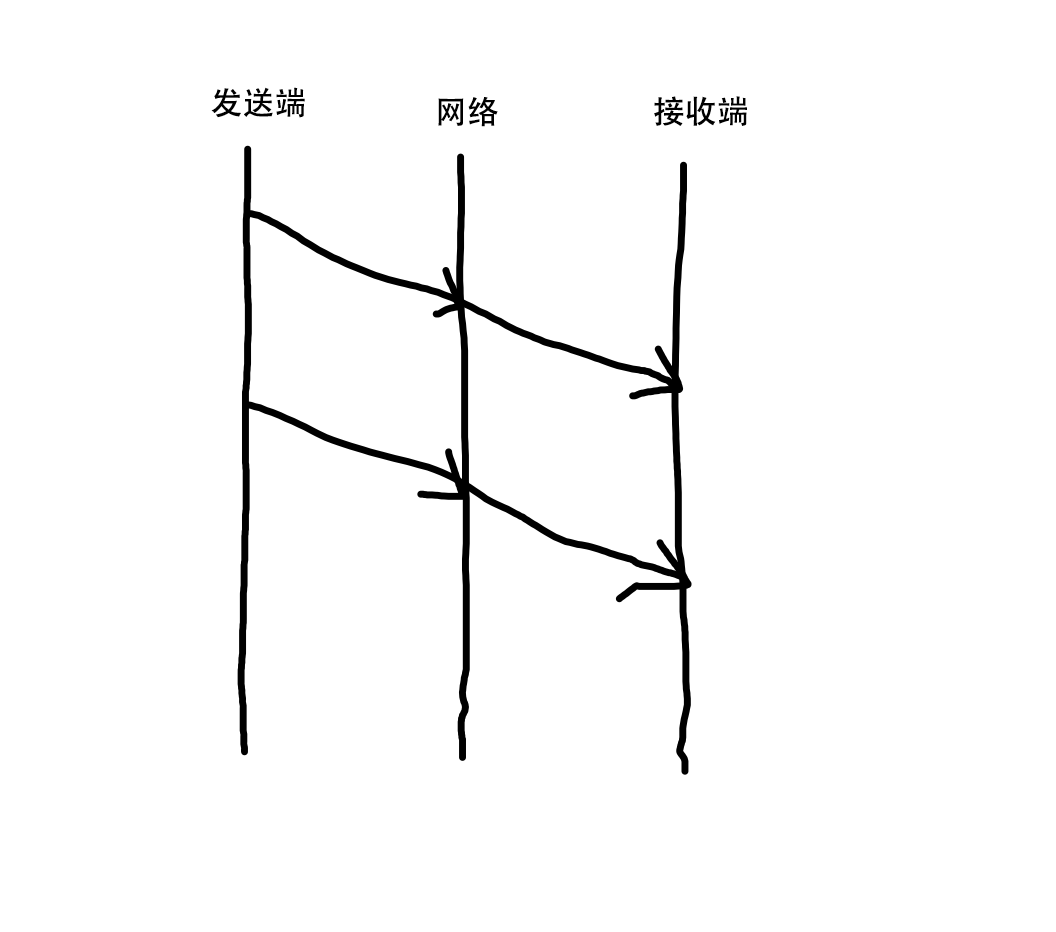
正常情况下网络时延:
拥塞情况下网络时延:
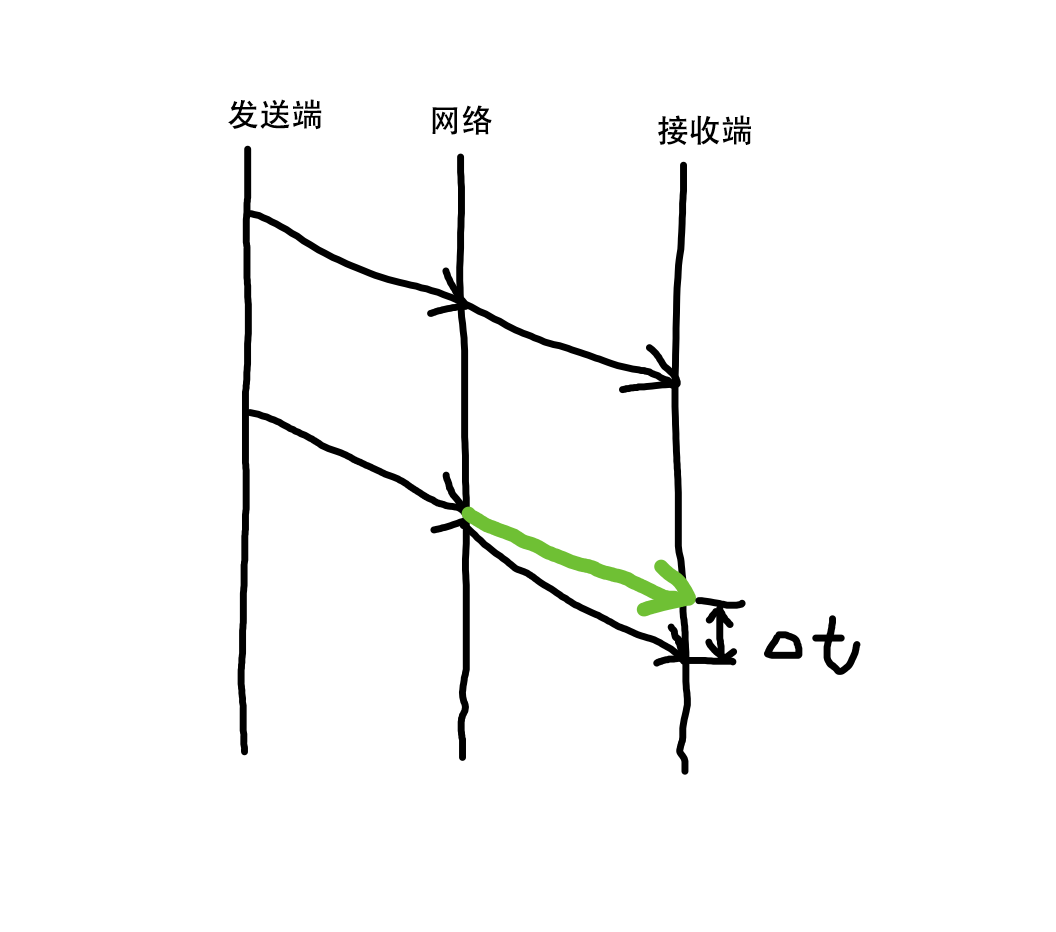
第一张图为正常情况下,此时没有拥塞,时延梯度 delta t = 0。图二如无网络拥塞包应该按绿线时间到达,此时发生了网络拥塞,到达时间比预定时间晚,此时 delta t 大于 0。
时延梯度经过平滑计算后,WebRTC 用最小二乘法计算出一个斜率,此斜率代表了网络趋势。最小二乘法公式如下:
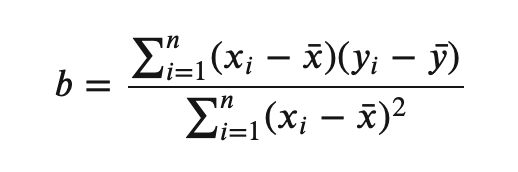
代码如下:
absl::optional<double> LinearFitSlope(
const std::deque<TrendlineEstimator::PacketTiming>& packets) {
RTC_DCHECK(packets.size() >= 2);
// Compute the "center of mass".
double sum_x = 0;
double sum_y = 0;
for (const auto& packet : packets) {
sum_x += packet.arrival_time_ms;
sum_y += packet.smoothed_delay_ms;
}
double x_avg = sum_x / packets.size();
double y_avg = sum_y / packets.size();
// Compute the slope k = \sum (x_i-x_avg)(y_i-y_avg) / \sum (x_i-x_avg)^2
double numerator = 0;
double denominator = 0;
for (const auto& packet : packets) {
double x = packet.arrival_time_ms;
double y = packet.smoothed_delay_ms;
numerator += (x - x_avg) * (y - y_avg);
denominator += (x - x_avg) * (x - x_avg);
}
if (denominator == 0)
return absl::nullopt;
return numerator / denominator;
}
探测网络状态
在计算得到 trendline 值后 WebRTC 通过动态阈值 threshold_ 进行判断拥塞程度,trendline 乘以周期包组个数再乘以一个放大系数就是 modified_trend。 threshold_ 是一个动态阀值,动态调整是为了改变它对网络状态的敏感度。如果阀值是固定的,它可能较大或较小。较大的话它对于网络变化不敏感,和基于丢包的拥塞控制竞争时可能会被饿死。较小的话可能经常检测出网络过载,频繁切换网络状态。
计算出 modified_trend 后,WebRTC 使用一个有限状态机进行状态切换,代码如下:
void TrendlineEstimator::Detect(double trend, double ts_delta, int64_t now_ms) {
if (num_of_deltas_ < 2) {
hypothesis_ = BandwidthUsage::kBwNormal;
return;
}
// 使用放大系数是因为一般情况下,trend 较小,不便于计算
const double modified_trend =
std::min(num_of_deltas_, kMinNumDeltas) * trend * threshold_gain_;
prev_modified_trend_ = modified_trend;
BWE_TEST_LOGGING_PLOT(1, "T", now_ms, modified_trend);
BWE_TEST_LOGGING_PLOT(1, "threshold", now_ms, threshold_);
if (modified_trend > threshold_) {
if (time_over_using_ == -1) {
// Initialize the timer. Assume that we've been
// over-using half of the time since the previous
// sample.
time_over_using_ = ts_delta / 2;
} else {
// Increment timer
time_over_using_ += ts_delta;
}
overuse_counter_++;
if (time_over_using_ > overusing_time_threshold_ && overuse_counter_ > 1) {
if (trend >= prev_trend_) {
time_over_using_ = 0;
overuse_counter_ = 0;
hypothesis_ = BandwidthUsage::kBwOverusing;
}
}
} else if (modified_trend < -threshold_) {
time_over_using_ = -1;
overuse_counter_ = 0;
hypothesis_ = BandwidthUsage::kBwUnderusing;
} else {
time_over_using_ = -1;
overuse_counter_ = 0;
hypothesis_ = BandwidthUsage::kBwNormal;
}
prev_trend_ = trend;
UpdateThreshold(modified_trend, now_ms);
}
目标带宽计算
目标带宽计算使用的是 AimdRateControl,Aimd 的全称是 Additive Increase Multiplicative Decrease,意思是和式增加,积式减少。
AimdRateControl::Update
DataRate AimdRateControl::Update(const RateControlInput* input,
Timestamp at_time) {
RTC_CHECK(input);
// 初始化
if (!bitrate_is_initialized_) {
const TimeDelta kInitializationTime = TimeDelta::Seconds(5);
RTC_DCHECK_LE(kBitrateWindowMs, kInitializationTime.ms());
if (time_first_throughput_estimate_.IsInfinite()) {
if (input->estimated_throughput)
time_first_throughput_estimate_ = at_time;
} else if (at_time - time_first_throughput_estimate_ >
kInitializationTime &&
input->estimated_throughput) {
current_bitrate_ = *input->estimated_throughput;
bitrate_is_initialized_ = true;
}
}
ChangeBitrate(*input, at_time);
return current_bitrate_;
}
AimdRateControl::ChangeBitrate
void AimdRateControl::ChangeBitrate(const RateControlInput& input,
Timestamp at_time) {
...
// 根据网络状态,切换码率控制状态
ChangeState(input, at_time);
// 码率上限限制到目前的 1.5 倍
const DataRate troughput_based_limit =
1.5 * estimated_throughput + DataRate::KilobitsPerSec(10);
switch (rate_control_state_) {
case kRcHold:
// 保持,直接返回
break;
case kRcIncrease:
// 超出目标上界,复位
if (estimated_throughput > link_capacity_.UpperBound())
link_capacity_.Reset();
// 当前码率小于 limit,且没有发生 alr
if (current_bitrate_ < troughput_based_limit &&
!(send_side_ && in_alr_ && no_bitrate_increase_in_alr_)) {
DataRate increased_bitrate = DataRate::MinusInfinity();
if (link_capacity_.has_estimate()) {
// 如果目标码率超过 link_capacity 的 bound 就会复位
// 当前码率接近带宽上限时,谨慎使用加性增加
DataRate additive_increase =
AdditiveRateIncrease(at_time, time_last_bitrate_change_);
increased_bitrate = current_bitrate_ + additive_increase;
} else {
// 还未估计出 link_capacity,可以使用乘性增加
DataRate multiplicative_increase = MultiplicativeRateIncrease(
at_time, time_last_bitrate_change_, current_bitrate_);
increased_bitrate = current_bitrate_ + multiplicative_increase;
}
new_bitrate = std::min(increased_bitrate, troughput_based_limit);
}
time_last_bitrate_change_ = at_time;
break;
case kRcDecrease: {
DataRate decreased_bitrate = DataRate::PlusInfinity();
// 为了避免自己产生 delay,使用 0.85 系数乘以当前吞吐量
decreased_bitrate = estimated_throughput * beta_;
if (decreased_bitrate > current_bitrate_ && !link_capacity_fix_) {
if (link_capacity_.has_estimate()) {
decreased_bitrate = beta_ * link_capacity_.estimate();
}
}
if (estimate_bounded_backoff_ && network_estimate_) {
decreased_bitrate = std::max(
decreased_bitrate, network_estimate_->link_capacity_lower * beta_);
}
// 避免 over-using 状态下的增加,新的码率使用当前码率和计算出的 decreased_bitrate 中的较小值
if (decreased_bitrate < current_bitrate_) {
new_bitrate = decreased_bitrate;
}
if (bitrate_is_initialized_ && estimated_throughput < current_bitrate_) {
if (!new_bitrate.has_value()) {
last_decrease_ = DataRate::Zero();
} else {
last_decrease_ = current_bitrate_ - *new_bitrate;
}
}
if (estimated_throughput < link_capacity_.LowerBound()) {
// The current throughput is far from the estimated link capacity. Clear
// the estimate to allow an immediate update in OnOveruseDetected.
link_capacity_.Reset();
}
bitrate_is_initialized_ = true;
link_capacity_.OnOveruseDetected(estimated_throughput);
// Stay on hold until the pipes are cleared.
rate_control_state_ = kRcHold;
time_last_bitrate_change_ = at_time;
time_last_bitrate_decrease_ = at_time;
break;
}
default:
assert(false);
}
current_bitrate_ = ClampBitrate(new_bitrate.value_or(current_bitrate_));
}
ChangeBitrate 中先根据网络状态计算出码率控制状态,再根据控制状态计算目标码率
ChangeState 是根据网络状态计算码率控制状态,码率控制状态有三种:保持、增加、减少。 当Overuse发生时,无论什么状态都进入减少。 当Underuse发生时,无论什么状态都进入保持状态。 当Normal发生时,在保持阶段,将进入增长。 代码如下:
AimdRateControl::ChangeState
void AimdRateControl::ChangeState(const RateControlInput& input,
Timestamp at_time) {
switch (input.bw_state) {
case BandwidthUsage::kBwNormal:
if (rate_control_state_ == kRcHold) {
time_last_bitrate_change_ = at_time;
rate_control_state_ = kRcIncrease;
}
break;
case BandwidthUsage::kBwOverusing:
if (rate_control_state_ != kRcDecrease) {
rate_control_state_ = kRcDecrease;
}
break;
case BandwidthUsage::kBwUnderusing:
rate_control_state_ = kRcHold;
break;
default:
assert(false);
}
}
乘性增加
DataRate AimdRateControl::MultiplicativeRateIncrease(
Timestamp at_time,
Timestamp last_time,
DataRate current_bitrate) const {
double alpha = 1.08;
if (last_time.IsFinite()) {
auto time_since_last_update = at_time - last_time;
// 时间差作为系数(不大于1.0),1.08 作为底数
alpha = pow(alpha, std::min(time_since_last_update.seconds<double>(), 1.0));
}
// 码率增加值为 1000 和 current_bitrate * (alpha - 1.0) 中较大值
DataRate multiplicative_increase =
std::max(current_bitrate * (alpha - 1.0), DataRate::BitsPerSec(1000));
return multiplicative_increase;
}
加性增加
DataRate AimdRateControl::AdditiveRateIncrease(Timestamp at_time,
Timestamp last_time) const {
double time_period_seconds = (at_time - last_time).seconds<double>();
double data_rate_increase_bps =
GetNearMaxIncreaseRateBpsPerSecond() * time_period_seconds;
return DataRate::BitsPerSec(data_rate_increase_bps);
}
TargetTransferRate 计算
struct TargetTransferRate {
Timestamp at_time = Timestamp::PlusInfinity();
// The estimate on which the target rate is based on.
NetworkEstimate network_estimate;
DataRate target_rate = DataRate::Zero();
DataRate stable_target_rate = DataRate::Zero();
double cwnd_reduce_ratio = 0;
};
TargetTransferRate 中有两个码率值,target_rate 和 stable_target_rate
更新目标码率
WebRTC 会综合 DelayBasedBwe 和 LinkCapacityTracker 计算出 TargetTransferRate,再据此计算出 target_bitrate 更新到 Sender、Endoder 模块。
Audio 码率更新
uint32_t AudioSendStream::OnBitrateUpdated(BitrateAllocationUpdate update) {
RTC_DCHECK_RUN_ON(worker_queue_);
// Pick a target bitrate between the constraints. Overrules the allocator if
// it 1) allocated a bitrate of zero to disable the stream or 2) allocated a
// higher than max to allow for e.g. extra FEC.
auto constraints = GetMinMaxBitrateConstraints();
update.target_bitrate.Clamp(constraints.min, constraints.max);
update.stable_target_bitrate.Clamp(constraints.min, constraints.max);
channel_send_->OnBitrateAllocation(update);
// The amount of audio protection is not exposed by the encoder, hence
// always returning 0.
return 0;
}
void ChannelSend::OnBitrateAllocation(BitrateAllocationUpdate update) {
// This method can be called on the worker thread, module process thread
// or on a TaskQueue via VideoSendStreamImpl::OnEncoderConfigurationChanged.
// TODO(solenberg): Figure out a good way to check this or enforce calling
// rules.
// RTC_DCHECK(worker_thread_checker_.IsCurrent() ||
// module_process_thread_checker_.IsCurrent());
rtc::CritScope lock(&bitrate_crit_section_);
// 编码器设置目标码率
CallEncoder([&](AudioEncoder* encoder) {
encoder->OnReceivedUplinkAllocation(update);
});
retransmission_rate_limiter_->SetMaxRate(update.target_bitrate.bps());
configured_bitrate_bps_ = update.target_bitrate.bps();
}
Video 码率更新
uint32_t VideoSendStreamImpl::OnBitrateUpdated(BitrateAllocationUpdate update) {
RTC_DCHECK_RUN_ON(worker_queue_);
RTC_DCHECK(rtp_video_sender_->IsActive())
<< "VideoSendStream::Start has not been called.";
// When the BWE algorithm doesn't pass a stable estimate, we'll use the
// unstable one instead.
if (update.stable_target_bitrate.IsZero()) {
update.stable_target_bitrate = update.target_bitrate;
}
// sender 更新目标码率
rtp_video_sender_->OnBitrateUpdated(update, stats_proxy_->GetSendFrameRate());
...
// 编码器更新目标码率
video_stream_encoder_->OnBitrateUpdated(
encoder_target_rate, encoder_stable_target_rate, link_allocation,
rtc::dchecked_cast<uint8_t>(update.packet_loss_ratio * 256),
update.round_trip_time.ms(), update.cwnd_reduce_ratio);
stats_proxy_->OnSetEncoderTargetRate(encoder_target_rate_bps_);
return protection_bitrate_bps;
}