前言
ViewRootImpl 实现了 ViewParent 接口,作为整个控件树的根部,它是控件正常运行的动力所在。控件的测量、布局、绘制要以及事件的派发都要经过 ViewRootImpl。我们分几个小节学习一下 ViewRootImpl,本节先来看一下它的构造方法和重要成员。
构造方法
ViewRootImpl 创建于 WindowManagerGolbal 的 addView 方法,而调用 addView() 的线程就是 ViewRootImpl 所掌控的控件树的 UI 线程。ViewRootImpl 的构造方法主要是初始化一些重要成员,我们来看一下:
public ViewRootImpl(Context context, Display display) {
mContext = context;
//从 WindowManagerGlobal 中获取一个 WindowSession 实例,它是 ViewROotImpl 和 WMS 进行通信的代理。
mWindowSession = WindowManagerGlobal.getWindowSession();
//保存 display 在后面 setView 调用中将会把窗口添加到这个 Display 上。
mDisplay = display;
mBasePackageName = context.getBasePackageName();
// 处理控件树的请求时 measure,layout,draw 会检查发起请求的线程和这个这个线程是否相同,如不同,抛出异常
mThread = Thread.currentThread();
mLocation = new WindowLeaked(null);
mLocation.fillInStackTrace();
mWidth = -1;
mHeight = -1;
//收集窗口中的无效区域,所谓无效区域是数据或状态发生改变时需要重绘的区域
mDirty = new Rect();
mTempRect = new Rect();
mVisRect = new Rect();
//当前窗口的位置和尺寸,于 WMS 中的 WindowState.mFrame 保持一致。
mWinFrame = new Rect();
mWindow = new W(this);
mTargetSdkVersion = context.getApplicationInfo().targetSdkVersion;
mViewVisibility = View.GONE;
mTransparentRegion = new Region();
mPreviousTransparentRegion = new Region();
mFirst = true; // true for the first time the view is added
mAdded = false;
//创建 mAttachInfo,AttachInfo 是控件系统中很重要的对象,它存储了当前控件树所依附的窗口的各种有用信息,并且会派发给每一个控件
mAttachInfo = new View.AttachInfo(mWindowSession, mWindow, display, this, mHandler, this,
context);
mAccessibilityManager = AccessibilityManager.getInstance(context);
mAccessibilityManager.addAccessibilityStateChangeListener(
mAccessibilityInteractionConnectionManager, mHandler);
mHighContrastTextManager = new HighContrastTextManager();
mAccessibilityManager.addHighTextContrastStateChangeListener(
mHighContrastTextManager, mHandler);
mViewConfiguration = ViewConfiguration.get(context);
mDensity = context.getResources().getDisplayMetrics().densityDpi;
mNoncompatDensity = context.getResources().getDisplayMetrics().noncompatDensityDpi;
mFallbackEventHandler = new PhoneFallbackEventHandler(context);
// 创建一个依附于当前线程,即主线程的 Choreographer
mChoreographer = Choreographer.getInstance();
mDisplayManager = (DisplayManager)context.getSystemService(Context.DISPLAY_SERVICE);
if (!sCompatibilityDone) {
sAlwaysAssignFocus = mTargetSdkVersion < Build.VERSION_CODES.P;
sCompatibilityDone = true;
}
loadSystemProperties();
}
在构造函数之外,还有两个重要的成员被直接初始化:
-
mHandler 类型为 ViewRootHandler,它依附于主线程,用于将某些操作调度到主线程执行。和 mChoreographer 不同,mChoreographer 由垂直同步事件驱动,主要处理重绘相关的操作。而 mHandler 是为了将发生在其他线程上的事件安排在主线程上执行。
- mSurface 类型为 Surface,采用无参构造函数构造的一个 Surface 实例。mSurface 此时是一个没有任何内容的空壳子,在 WMS 通过 relayoutWindow() 为其分配一块 Surface 之前尚不能使用。
- mWinFrame、mPendingContentInset、mPendingVisibleInset 以及 mWidth 和 mHeight。这几个成员存储了窗口布局相关的信息。其中 mWinFrame、mPendingContentInset、mPendingVisibleInset 与窗口在 WMS 中的 Frame、ContentInsets、VisibleInsets 是保持同步的。 mWinFrame 记录了窗口在 WMS 中的尺寸信息,mWidth 和 mHeight 记录了窗口在 ViewRootImpl 中的尺寸,二者在大部分情况下是相同的。当窗口在 WMS 中被重新布局导致尺寸变化时,mWinFrame 首先会被 IWindow.Stub.resize()回掉更新,此时 mWinFrame 与 mWidth/mHeight 产生差异,ViewRootImpl 即可得知需要对控件树进行重新布局以适应窗口的变化。
ViewRootImpl 在其构造方法中初始化了一系列成员变量,然而其创建过程仍未完成。仅在为其指定了一个控件树进行管理,并向 WMS 中添加了一个新的窗口之后,ViewRootImpl 的角色才算真正确定下来。
ViewRootImpl#setView
/**
* We have one child
*/
public void setView(View view, WindowManager.LayoutParams attrs, View panelParentView) {
synchronized (this) {
if (mView == null) {
//mView 保存控件树的根
mView = view;
mAttachInfo.mDisplayState = mDisplay.getState();
mDisplayManager.registerDisplayListener(mDisplayListener, mHandler);
mViewLayoutDirectionInitial = mView.getRawLayoutDirection();
mFallbackEventHandler.setView(view);
//mWindowAttributes 保存了窗口对应的 LayoutParam
mWindowAttributes.copyFrom(attrs);
if (mWindowAttributes.packageName == null) {
mWindowAttributes.packageName = mBasePackageName;
}
attrs = mWindowAttributes;
setTag();
if (DEBUG_KEEP_SCREEN_ON && (mClientWindowLayoutFlags
& WindowManager.LayoutParams.FLAG_KEEP_SCREEN_ON) != 0
&& (attrs.flags&WindowManager.LayoutParams.FLAG_KEEP_SCREEN_ON) == 0) {
Slog.d(mTag, "setView: FLAG_KEEP_SCREEN_ON changed from true to false!");
}
// Keep track of the actual window flags supplied by the client.
mClientWindowLayoutFlags = attrs.flags;
setAccessibilityFocus(null, null);
if (view instanceof RootViewSurfaceTaker) {
mSurfaceHolderCallback =
((RootViewSurfaceTaker)view).willYouTakeTheSurface();
if (mSurfaceHolderCallback != null) {
mSurfaceHolder = new TakenSurfaceHolder();
mSurfaceHolder.setFormat(PixelFormat.UNKNOWN);
mSurfaceHolder.addCallback(mSurfaceHolderCallback);
}
}
// Compute surface insets required to draw at specified Z value.
// TODO: Use real shadow insets for a constant max Z.
if (!attrs.hasManualSurfaceInsets) {
attrs.setSurfaceInsets(view, false /*manual*/, true /*preservePrevious*/);
}
CompatibilityInfo compatibilityInfo =
mDisplay.getDisplayAdjustments().getCompatibilityInfo();
mTranslator = compatibilityInfo.getTranslator();
// If the application owns the surface, don't enable hardware acceleration
if (mSurfaceHolder == null) {
// While this is supposed to enable only, it can effectively disable
// the acceleration too.
enableHardwareAcceleration(attrs);
final boolean useMTRenderer = MT_RENDERER_AVAILABLE
&& mAttachInfo.mThreadedRenderer != null;
if (mUseMTRenderer != useMTRenderer) {
// Shouldn't be resizing, as it's done only in window setup,
// but end just in case.
endDragResizing();
mUseMTRenderer = useMTRenderer;
}
}
boolean restore = false;
if (mTranslator != null) {
mSurface.setCompatibilityTranslator(mTranslator);
restore = true;
attrs.backup();
mTranslator.translateWindowLayout(attrs);
}
if (DEBUG_LAYOUT) Log.d(mTag, "WindowLayout in setView:" + attrs);
if (!compatibilityInfo.supportsScreen()) {
attrs.privateFlags |= WindowManager.LayoutParams.PRIVATE_FLAG_COMPATIBLE_WINDOW;
mLastInCompatMode = true;
}
mSoftInputMode = attrs.softInputMode;
mWindowAttributesChanged = true;
mWindowAttributesChangesFlag = WindowManager.LayoutParams.EVERYTHING_CHANGED;
mAttachInfo.mRootView = view;
mAttachInfo.mScalingRequired = mTranslator != null;
mAttachInfo.mApplicationScale =
mTranslator == null ? 1.0f : mTranslator.applicationScale;
if (panelParentView != null) {
mAttachInfo.mPanelParentWindowToken
= panelParentView.getApplicationWindowToken();
}
mAdded = true;
int res; /* = WindowManagerImpl.ADD_OKAY; */
// Schedule the first layout -before- adding to the window
// manager, to make sure we do the relayout before receiving
// any other events from the system.
requestLayout();
//mInputChannel 是窗口接收来自 InputDispatcher 的输入事件管道
if ((mWindowAttributes.inputFeatures
& WindowManager.LayoutParams.INPUT_FEATURE_NO_INPUT_CHANNEL) == 0) {
mInputChannel = new InputChannel();
}
mForceDecorViewVisibility = (mWindowAttributes.privateFlags
& PRIVATE_FLAG_FORCE_DECOR_VIEW_VISIBILITY) != 0;
//将窗口添加到 WMS 中,完成这个操作之后 mWindow 已经被添加到指定的 Display 中,而且 mInputChannel 已经准备好接受事件,只是这个窗口还没有进行 relayout() 因此它没有有效的 Surface 进行绘制。
try {
mOrigWindowType = mWindowAttributes.type;
mAttachInfo.mRecomputeGlobalAttributes = true;
collectViewAttributes();
res = mWindowSession.addToDisplay(mWindow, mSeq, mWindowAttributes,
getHostVisibility(), mDisplay.getDisplayId(), mWinFrame,
mAttachInfo.mContentInsets, mAttachInfo.mStableInsets,
mAttachInfo.mOutsets, mAttachInfo.mDisplayCutout, mInputChannel);
} catch (RemoteException e) {
mAdded = false;
mView = null;
mAttachInfo.mRootView = null;
mInputChannel = null;
mFallbackEventHandler.setView(null);
unscheduleTraversals();
setAccessibilityFocus(null, null);
throw new RuntimeException("Adding window failed", e);
} finally {
if (restore) {
attrs.restore();
}
}
if (mTranslator != null) {
mTranslator.translateRectInScreenToAppWindow(mAttachInfo.mContentInsets);
}
mPendingOverscanInsets.set(0, 0, 0, 0);
mPendingContentInsets.set(mAttachInfo.mContentInsets);
mPendingStableInsets.set(mAttachInfo.mStableInsets);
mPendingDisplayCutout.set(mAttachInfo.mDisplayCutout);
mPendingVisibleInsets.set(0, 0, 0, 0);
mAttachInfo.mAlwaysConsumeNavBar =
(res & WindowManagerGlobal.ADD_FLAG_ALWAYS_CONSUME_NAV_BAR) != 0;
mPendingAlwaysConsumeNavBar = mAttachInfo.mAlwaysConsumeNavBar;
if (DEBUG_LAYOUT) Log.v(mTag, "Added window " + mWindow);
if (res < WindowManagerGlobal.ADD_OKAY) {
mAttachInfo.mRootView = null;
mAdded = false;
mFallbackEventHandler.setView(null);
unscheduleTraversals();
setAccessibilityFocus(null, null);
switch (res) {
case WindowManagerGlobal.ADD_BAD_APP_TOKEN:
case WindowManagerGlobal.ADD_BAD_SUBWINDOW_TOKEN:
throw new WindowManager.BadTokenException(
"Unable to add window -- token " + attrs.token
+ " is not valid; is your activity running?");
case WindowManagerGlobal.ADD_NOT_APP_TOKEN:
throw new WindowManager.BadTokenException(
"Unable to add window -- token " + attrs.token
+ " is not for an application");
case WindowManagerGlobal.ADD_APP_EXITING:
throw new WindowManager.BadTokenException(
"Unable to add window -- app for token " + attrs.token
+ " is exiting");
case WindowManagerGlobal.ADD_DUPLICATE_ADD:
throw new WindowManager.BadTokenException(
"Unable to add window -- window " + mWindow
+ " has already been added");
case WindowManagerGlobal.ADD_STARTING_NOT_NEEDED:
// Silently ignore -- we would have just removed it
// right away, anyway.
return;
case WindowManagerGlobal.ADD_MULTIPLE_SINGLETON:
throw new WindowManager.BadTokenException("Unable to add window "
+ mWindow + " -- another window of type "
+ mWindowAttributes.type + " already exists");
case WindowManagerGlobal.ADD_PERMISSION_DENIED:
throw new WindowManager.BadTokenException("Unable to add window "
+ mWindow + " -- permission denied for window type "
+ mWindowAttributes.type);
case WindowManagerGlobal.ADD_INVALID_DISPLAY:
throw new WindowManager.InvalidDisplayException("Unable to add window "
+ mWindow + " -- the specified display can not be found");
case WindowManagerGlobal.ADD_INVALID_TYPE:
throw new WindowManager.InvalidDisplayException("Unable to add window "
+ mWindow + " -- the specified window type "
+ mWindowAttributes.type + " is not valid");
}
throw new RuntimeException(
"Unable to add window -- unknown error code " + res);
}
if (view instanceof RootViewSurfaceTaker) {
mInputQueueCallback =
((RootViewSurfaceTaker)view).willYouTakeTheInputQueue();
}
if (mInputChannel != null) {
if (mInputQueueCallback != null) {
mInputQueue = new InputQueue();
mInputQueueCallback.onInputQueueCreated(mInputQueue);
}
//创建 mInputEventReceiver 用于接收输入事件,注意 Looper,事件被直接发到主线程中
mInputEventReceiver = new WindowInputEventReceiver(mInputChannel,
Looper.myLooper());
}
// 将 ViewRootImpl 作为控件树的 parent,这个很有用,invalidate()、requestLayout() 都需要回溯到 ViewRootImpl 进行触发。
view.assignParent(this);
mAddedTouchMode = (res & WindowManagerGlobal.ADD_FLAG_IN_TOUCH_MODE) != 0;
mAppVisible = (res & WindowManagerGlobal.ADD_FLAG_APP_VISIBLE) != 0;
if (mAccessibilityManager.isEnabled()) {
mAccessibilityInteractionConnectionManager.ensureConnection();
}
if (view.getImportantForAccessibility() == View.IMPORTANT_FOR_ACCESSIBILITY_AUTO) {
view.setImportantForAccessibility(View.IMPORTANT_FOR_ACCESSIBILITY_YES);
}
// Set up the input pipeline.
CharSequence counterSuffix = attrs.getTitle();
mSyntheticInputStage = new SyntheticInputStage();
InputStage viewPostImeStage = new ViewPostImeInputStage(mSyntheticInputStage);
InputStage nativePostImeStage = new NativePostImeInputStage(viewPostImeStage,
"aq:native-post-ime:" + counterSuffix);
InputStage earlyPostImeStage = new EarlyPostImeInputStage(nativePostImeStage);
InputStage imeStage = new ImeInputStage(earlyPostImeStage,
"aq:ime:" + counterSuffix);
InputStage viewPreImeStage = new ViewPreImeInputStage(imeStage);
InputStage nativePreImeStage = new NativePreImeInputStage(viewPreImeStage,
"aq:native-pre-ime:" + counterSuffix);
mFirstInputStage = nativePreImeStage;
mFirstPostImeInputStage = earlyPostImeStage;
mPendingInputEventQueueLengthCounterName = "aq:pending:" + counterSuffix;
}
}
}
至此,ViewRootImpl 中所有成员都已经初始化完毕,它们分类如下:
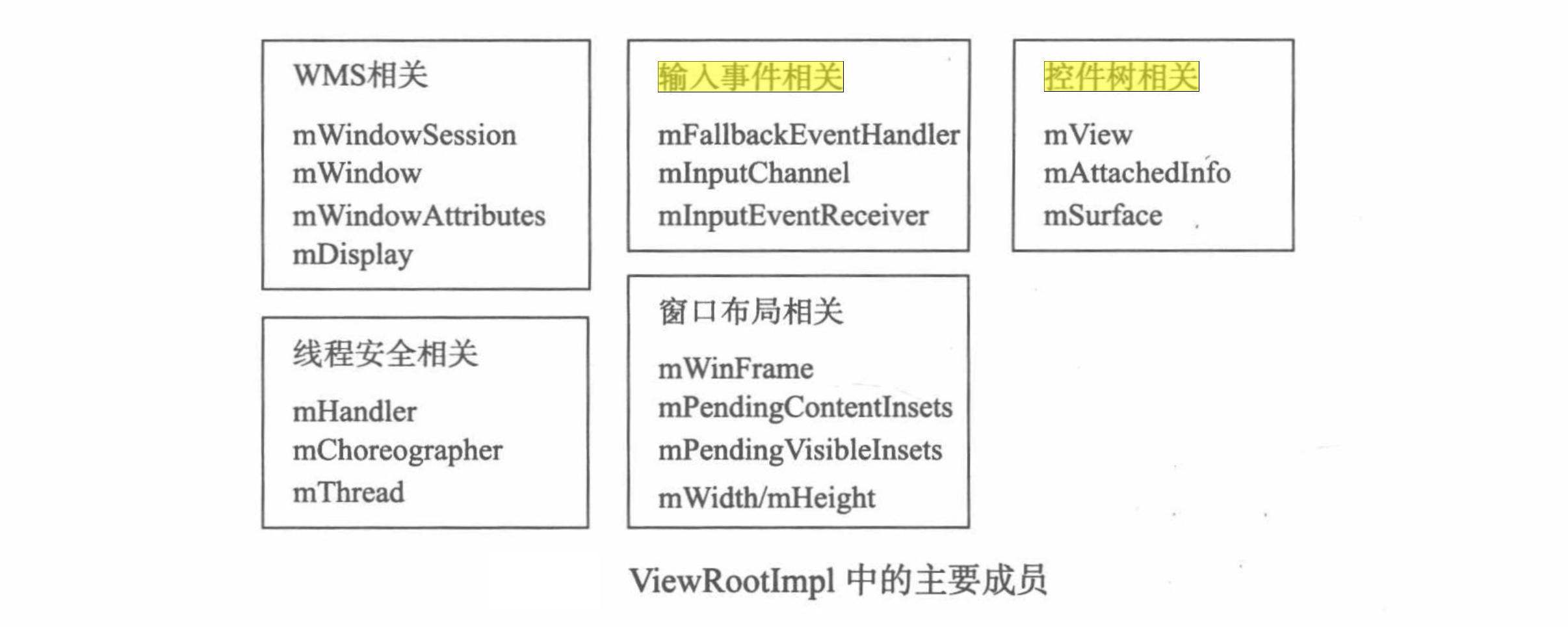
总结
- ViewRootImpl 在构造的时候保存了创建它的线程,后续在更新 UI 时会检查调用线程和创建它的线程是否一致。
- setView 中会触发一次 requestLayout() ,实际上就是触发了 performTraversals()。目的是确保在「 window 被添加到 WindowManager」之前触发一次遍历,以便后续接收各种事件。
- setView 中通过 view.assignParent(this); 将自己设为 DecorView 的 Parent,自此 ViewRootImpl 真正成为了控件树的根,任一子 View 可以通过 getParent 回溯到 ViewRootImpl。因此 invalidate() 和 requestLayout() 等可以触发 performTraversals()。